 How often should you have an electrical safety inspection
How often should you have an electrical safety inspection

When it comes to electrical safety inspections, understanding and complying with legal requirements is non-negotiable. For property owners, staying informed about these regulations is crucial to ensure the safety of tenants and the integrity of the property.
Legal Requirements for Electrical Safety Inspections
The law mandates regular electrical inspections to safeguard against potential hazards. In England, the Private Rented Sector (England) Regulations 2020 stipulate that landlords must have their properties inspected and tested by a qualified person at least every five years. This regulation is designed to ensure that electrical installations in rented residential properties are safe when tenants move in and maintained in a safe condition throughout the tenancy.
Impact of the Private Rented Sector Regulations on Inspection Intervals
These regulations have introduced a fixed timeline for inspections, making it easier for landlords to keep track of and schedule necessary checks. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and legal consequences.
Adherence to the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989
For businesses, the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989 dictate that all electrical systems must be maintained to prevent danger. This is not prescriptive about the frequency of inspections but emphasises a risk-based approach. Businesses must assess their electrical equipment’s risk level and use this to inform their maintenance and inspection schedules.
Ensuring Compliance with Electrical Safety Obligations
To ensure compliance, property owners should:
- Schedule regular inspections according to the type of property and its use.
- Employ a certified and competent electrician to conduct inspections and obtain an Electrical Installation Condition Report (EICR).
- Keep records of all safety checks and remedial work carried out.
- Stay updated on any changes in legislation that may affect inspection frequency or requirements.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can maintain a safe environment and avoid the legal repercussions of non-compliance.
Landlord Responsibilities for Electrical Safety
Landlords bear the crucial responsibility of ensuring the electrical safety of their properties. This duty is not only a matter of tenant welfare but also a legal mandate. Under the Private Rented Sector (England) Regulations 2020, landlords are required to provide tenants with an Electrical Installation Condition Report (EICR) every five years. This document is a comprehensive assessment of the electrical installation within the property and must be carried out by a qualified and competent person.
Ensuring Tenant Protection Through Regular Inspections
Regular electrical inspections serve as a preventive measure against potential hazards, safeguarding tenants from electrical risks. These inspections are designed to identify any deficiencies or defects that could lead to accidents or incidents. By proactively managing these risks, landlords contribute to the overall safety and well-being of their tenants.
Legal Implications of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with electrical safety standards can result in stringent consequences for landlords. Local authorities have the power to enforce compliance, and non-adherence may lead to substantial fines. It is imperative for landlords to understand that these regulations are in place not only to protect tenants but also to uphold the integrity of the property and the safety of the community at large.
Frequency of Electrical Installation Condition Reports
The frequency at which landlords must provide an EICR is set at a minimum of every five years. However, it is recommended to conduct inspections more frequently if there are concerns about the property’s electrical systems or if significant changes have been made to the installation. Landlords must remain vigilant and responsive to any signs of electrical deterioration to maintain compliance and ensure safety.
Enforcement of Electrical Safety by Local Authorities
Local authorities play a pivotal role in ensuring that electrical safety standards are met by property owners. They have the authority to enforce compliance through regular inspections and can impose penalties on those who fail to adhere to the regulations.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Property owners who do not comply with electrical safety regulations may face significant fines. These fines are not only punitive but also serve as a deterrent to prevent negligence regarding electrical safety. The exact amount can vary depending on the severity of the non-compliance and the local authority’s policies.
Supportive Measures for Compliance
Local authorities often provide guidance and resources to assist property owners in understanding their obligations. They may offer checklists, guidelines, and access to qualified professionals who can conduct the necessary inspections and tests.
Collaborating with Local Authorities
To maintain electrical safety and compliance, property owners are encouraged to proactively engage with local authorities. This collaboration can include regular communication, attending safety seminars, and promptly addressing any issues identified during inspections. By working together, property owners and local authorities can ensure a safer living and working environment for all occupants.
Clarifying Portable Appliance Testing (PAT)

Portable Appliance Testing (PAT) is often surrounded by misconceptions. One common myth is that PAT is an excessively frequent and mandatory requirement for all appliances, which is not the case. The reality is that PAT frequency should be determined by a risk-based assessment, considering factors such as the type of appliance, its use, and the environment in which it operates.
The Role of Visual Inspections in PAT
Visual inspections are a significant component of the PAT process. They are the initial step in identifying potential hazards with electrical appliances and can often reveal the most common faults. These inspections should be carried out by users regularly and by competent persons during formal PAT.
Determining PAT Frequency
The frequency of PAT is not set in stone but should be informed by the environment in which the appliance is used, the nature of the equipment, and the risk of damage or deterioration. For example, appliances used in a commercial kitchen may require more frequent testing than those in a low-risk office environment.
Integrating PAT into Electrical Safety Strategies
PAT is a critical element of a comprehensive electrical safety inspection strategy. It complements fixed wiring inspections and should be integrated into the overall maintenance schedule to ensure all aspects of electrical safety are addressed, thus safeguarding both property and personnel.
Implementing a Risk-Based Approach to Electrical Equipment Maintenance
A risk-based approach to electrical equipment maintenance is essential for ensuring safety and compliance with the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989. This approach requires a thorough assessment of potential electrical hazards associated with equipment and the environment in which it operates.
Key Components of Electrical Safety Risk Assessment
The risk assessment process involves identifying hazards, determining who may be harmed and how, evaluating risks, and deciding on precautions. It should also include a review of incident reports and maintenance records to inform the assessment of risk levels.
Determining Inspection and Testing Frequencies
There is no fixed testing frequency mandated by law; instead, businesses should assess the risks associated with their electrical equipment to determine appropriate intervals. Factors influencing this decision include the type of equipment, its age, frequency of use, and the environment it operates in.
Health and Safety Executive (HSE) Guidelines
The HSE provides guidelines for a risk-based approach to electrical safety, emphasising the importance of maintaining equipment to prevent danger. Businesses are advised to implement a regular inspection and testing schedule based on their risk assessment findings to ensure ongoing electrical safety.
Visual Checks: The First Line of Defence in Electrical Safety
Visual checks are a fundamental aspect of electrical safety, acting as the initial screening for potential hazards. These checks can quickly identify obvious signs of damage, wear, or misuse of electrical equipment, which are often the precursors to electrical failures or accidents.
Identifying Immediate Hazards
During visual checks, users should be vigilant for frayed cords, damaged insulation, cracked plug casings, and any signs of overheating, such as burn marks or unusual smells. These indicators can often be addressed immediately to prevent further risk.
Cultivating a Safety-First Culture
Encouraging a culture of safety among users is vital. When individuals are trained to recognise and report potential hazards, the likelihood of electrical accidents can be significantly reduced. This proactive approach to safety can lead to a more informed and responsive environment.
Resources for Effective Visual Checks
A variety of resources are available to empower users to conduct effective visual checks. These include safety checklists, instructional videos, and training sessions led by qualified professionals. Many organisations also provide in-house training to ensure that their staff can carry out these inspections competently and confidently.
Criteria for a Competent Electrical Tester

When it comes to electrical safety inspections, the competence of the individual conducting the testing is paramount. A competent person should possess a blend of education, experience, and certifications that align with industry standards.
Verifying Electrician Credentials
To verify an electrician’s credentials, property and business owners should request proof of qualifications, such as certification from a recognised industry body like the National Inspection Council for Electrical Installation Contracting (NICEIC). Additionally, checking for a history of completed inspections and references can provide assurance of the electrician’s proficiency.
Required Training and Equipment
A competent electrical tester must be trained in the use of specific test instruments and understand the safety protocols associated with electrical work. This includes knowledge of the latest wiring regulations and the ability to interpret the results of tests such as earth continuity, insulation resistance, and polarity checks.
Interpreting Test Results for Safety
Understanding test results is crucial for diagnosing potential electrical issues and implementing corrective actions. A competent person will be able to analyse the data from inspections, identify trends that may indicate underlying problems, and recommend solutions to ensure the ongoing safety and compliance of the electrical installation.
Systematic Approach to Electrical Maintenance

A systematic approach to electrical maintenance involves a structured plan that includes regular inspections, timely repairs, and consistent record-keeping. This proactive strategy is designed to identify and mitigate electrical risks before they escalate into more significant issues.
Tailoring Inspection Frequencies
Inspection frequencies should be customised based on the specific environment in which the electrical equipment operates and its usage patterns. High-risk environments, such as industrial settings with heavy machinery, may require more frequent inspections than residential properties.
Role of Maintenance Schemes in Electrical Safety
Maintenance schemes are integral to electrical safety, providing a framework for scheduled checks and procedures that ensure all components of an electrical system are functioning correctly and safely. These schemes should be developed in accordance with industry standards and legal requirements.
Developing a Compliant Maintenance Schedule
Property and business owners can develop a maintenance schedule that aligns with legal requirements by consulting the latest regulations, such as the Private Rented Sector (England) Regulations 2020 and the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989. It is advisable to work with certified electrical safety professionals to establish a schedule that not only meets legal standards but also addresses the unique needs of the property.
Essential Technical Tests for Electrical Safety Compliance

To ensure electrical safety compliance, several technical tests are routinely performed. These tests are critical for identifying potential risks and ensuring the integrity of electrical systems.
Core Electrical Safety Tests
- Earth Continuity: Confirms that the protective conductors are effectively connected to the necessary earthing points.
- Insulation Resistance: Measures the resistance of electrical insulation to prevent current leakage, which can lead to shocks and fires.
Additional Safety Measures
- Polarity Testing: Ensures that the electrical connections are correctly made and that the current flows in the intended direction.
- Residual Current Device (RCD) Testing: Verifies the functionality of RCDs, which are designed to prevent electric shock by rapidly disconnecting the current.
Advanced Techniques for Comprehensive Inspections
For a more thorough assessment of electrical safety, advanced techniques are employed:
- Thermal Imaging: Detects overheating components that could indicate electrical faults.
- Voltage Testing: Measures the voltage levels in electrical circuits to ensure they are operating within safe limits.
Staying Informed on Electrical Safety
Property and business owners can stay informed about the technical aspects of electrical safety by:
- Attending workshops and training sessions offered by electrical safety authorities.
- Subscribing to industry publications and updates from regulatory bodies like the Health and Safety Executive (HSE).
- Consulting with certified electricians who are up-to-date with the latest safety standards and testing methods.
Importance of Documentation for Electrical Safety Compliance
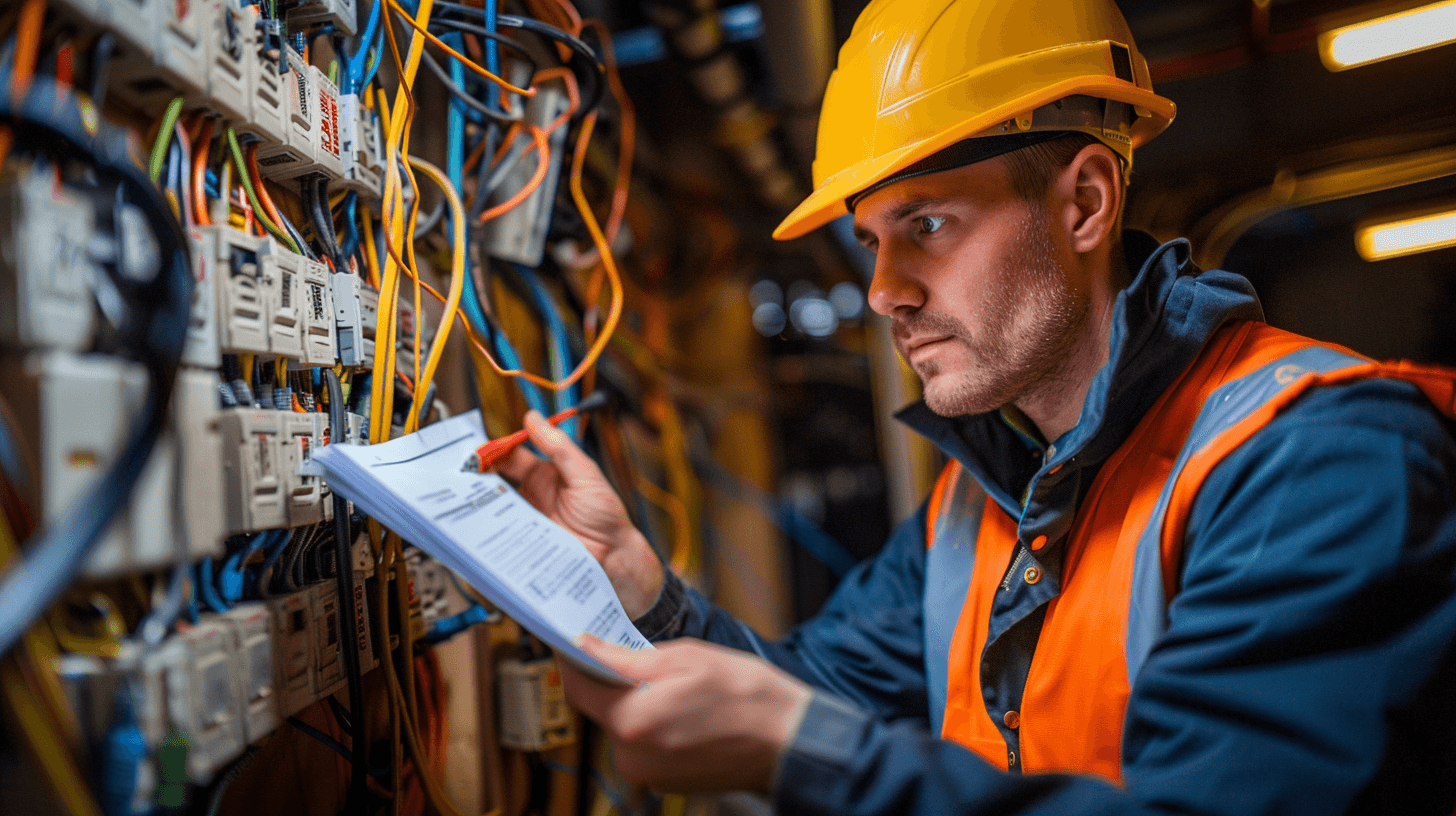
Accurate documentation is a cornerstone of electrical safety compliance. It serves as a record of all inspections, tests, and maintenance activities performed on electrical systems. The Electrical Installation Condition Report (EICR) is particularly critical as it provides a formal assessment of the electrical installation’s condition within a property.
Periodic Inspection Requirements
Periodic inspections are essential to ensure ongoing compliance with electrical safety standards. The frequency of these inspections is typically every five years for residential properties, but this can vary depending on the type of property, its use, and the results of previous inspections.
Record-Keeping in Electrical Safety
Maintaining precise records is vital for several reasons:
- It helps track the history of electrical systems, facilitating easier diagnosis of issues.
- It provides evidence of compliance with safety regulations, which is crucial in the event of an incident.
- It ensures that any identified issues have been addressed, contributing to the overall safety of the property.
Ensuring Documentation Meets Industry Standards
To ensure documentation meets industry standards, property and business owners should:
- Engage with certified electricians who are well-versed in the latest regulations.
- Use standardised forms and checklists for all inspections and maintenance activities.
- Keep all records organised and accessible for review by inspectors or maintenance personnel.
Criteria for Choosing an Electrical Service Provider

When selecting an electrical service provider, property and business owners should prioritise qualifications and certifications. A provider’s credentials are a testament to their expertise and commitment to safety standards.
Benefits of NICEIC Approval and ISO Certification
Choosing a provider with NICEIC approval and ISO certification offers several advantages:
- Assurance of Quality: These certifications indicate that the provider meets high standards of quality and safety.
- Compliance with Regulations: Certified providers are more likely to be up-to-date with current electrical regulations, ensuring legal compliance.
- Professionalism: Accredited providers are bound by a code of conduct, which typically guarantees a higher level of service and professionalism.
Comprehensive Electrical Services
A well-rounded electrical service provider should offer a broad spectrum of services, including:
- Emergency Repairs: Prompt response to urgent electrical issues.
- Installations: Up-to-date installation services that comply with the latest safety standards.
- Safety Inspections: Thorough inspections and testing to ensure electrical systems are safe and efficient.
All Service 4U: A Model of Excellence
All Service 4U exemplifies the ideal qualifications and services that property owners should seek:
- 24/7 Availability: Ensuring assistance is always at hand.
- NICEIC Approved: Demonstrating adherence to safety and service quality.
- ISO Certified: Commitment to consistent and reliable service delivery.
- Comprehensive Maintenance: Offering a suite of services that cater to all aspects of property maintenance.
Proactive Electrical Safety Management

Property and business owners are encouraged to adopt a proactive stance on electrical safety management. This involves scheduling regular safety inspections and staying informed about the latest electrical safety regulations. By doing so, owners can prevent potential hazards and ensure the longevity of their electrical systems.
Long-Term Benefits of Regular Electrical Safety Inspections
Regular electrical safety inspections offer numerous long-term benefits, including:
- Preventing Electrical Failures: Routine inspections can identify and rectify issues before they lead to costly failures.
- Ensuring Tenant Safety: Inspections help protect tenants from electrical hazards, thereby reducing liability risks.
- Maintaining Property Value: Up-to-date electrical systems are essential for preserving property value and attracting tenants.
All Service 4U’s Commitment to Electrical Safety
All Service 4U is dedicated to assisting property owners in upholding electrical safety standards. Their services include:
- 24/7 Emergency Response: Ensuring that help is available around the clock for urgent electrical issues.
- Certified Electricians: Providing peace of mind that all work is carried out by qualified professionals.
- Comprehensive Inspections: Conducting thorough inspections that meet all regulatory requirements.
Contacting All Service 4U
For electrical safety services, interested parties can contact All Service 4U via:
- Phone: Reaching out to their customer service team at 020 3627 0820.
- Email: Sending inquiries to their support email for detailed responses.
- Website: Visiting the All Service 4U website to request services or obtain more information.

